 To leave application form
To leave application form
The outfit is designed for effective application of anhydrous ammonia as basic nitrogen fertilizer. The applicator can be used to apply anhydrous ammonia upon soil preparation of any type (plowing, deep tilling, min-till, no-till). use of original tools provides for uniform and proper fertilization to a given depth with no losses of ammonia. The applicator is equipped with a distribution and ammonia application control system, developed by “Raven” (USA).
The applicator includes a cultivator with an effective width ranging from 8.2 to 10.2, tools and a storage trailer for ammonia transportation. Frame-mounted equipment: dosing systems “Raven”, distributing manifolds and supply tubes. The rate of application is pre-set on the control panel in the tractor cab, where a high-accuracy GPS navigation system is also installed.
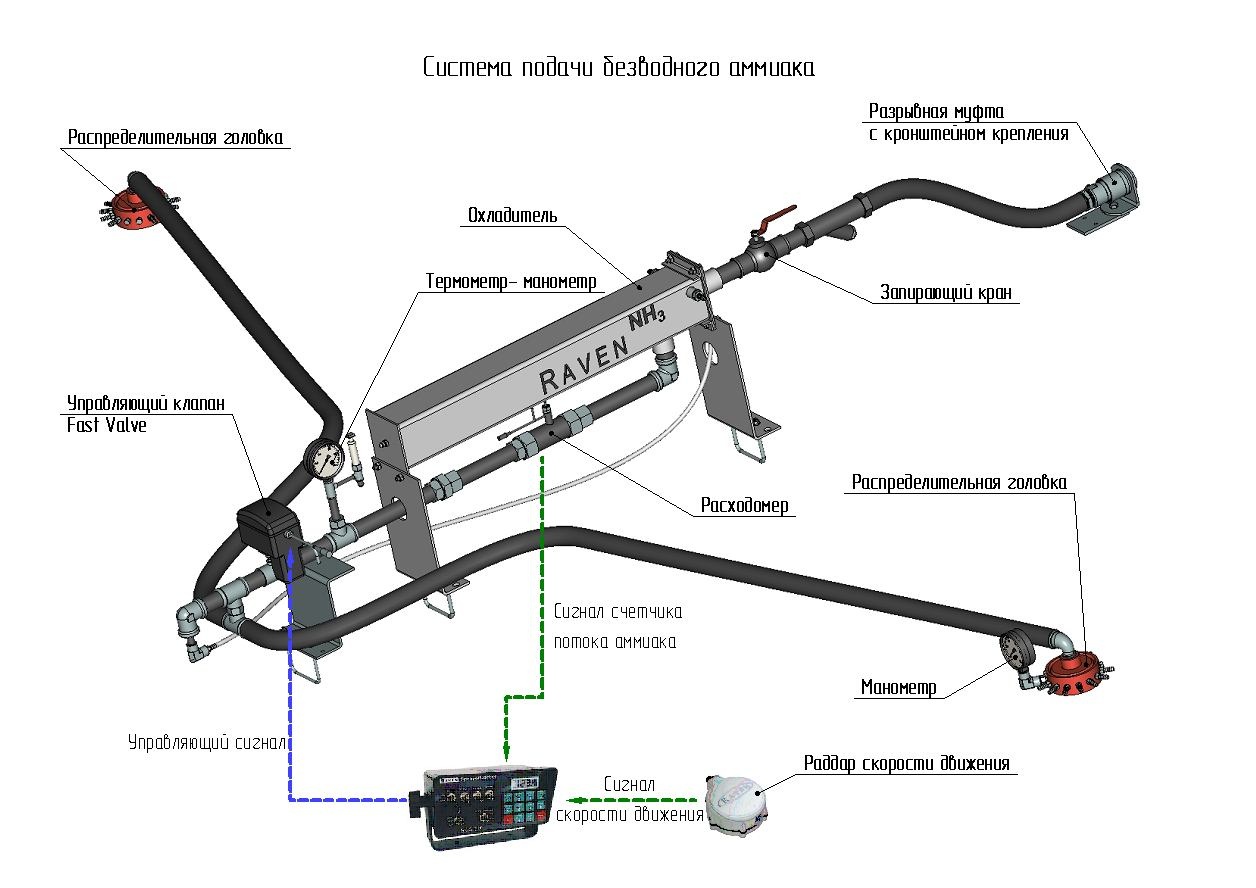
The system “Raven” consists of a cooler, ammonia flow meter, dosing valve, pressure and temperature monitoring devices, distribution heads and hoses.
Economical efficiency and agronomic effectiveness of anhydrous ammonia:
1. Pay-back time: one season only. The use of anhydrous ammonia, as opposed to ammonia nitrate (at the same rate of application and equal costs), is by max. 50% more beneficial; the rate of return of 1 ruble invested into this fertilizer ranges from 4 to 7 rubles, depending on a specific crop.
2. Yield enhancement by max. 30%, as compared with dry fertilizers.
No influence of extreme weather conditions (dry periods, rain showers and etc.). Ammonia is not washed out, as it binds to soils, and plants receive all nutritional substances required. As a comparison, ammonia nitrate remains active in dry conditions (if no precipitation) within two weeks only and exhibits a reverse, ‘moisture absorbing” effect. Ammonia nitrogen is stable, as negatively charged particles of clay and humus keep it within the soil. Ammonia takes its nitrate form progressively, which ensures its constant impact upon plants growing.
4. Anhydrous ammonia kills rodents, pests, wire worms, mold fungus and weed seeds, as they absorb nitrogen partially in spring.
5. Anhydrous ammonia is not harmful to microflora of soils, and losses are temporary and renewable. Higher concentrations of ammonia may result in partial sterilization of soils, where it’s applied. But within 7 – 10 days, microbial populations regenerate to reach their previous counts, even exceeding them, which results from improvement of nitrogenous nutrition.
6. Fewer dead plants (by 1.3 – 2.3 times less)
As opposed to broadcasting, which contributes to germination of weed seeds (especially, wild oats and pink family), continuous banding considerably reduces weed-seed germination. Furthermore, granules of dry fertilizers can get close to weeds, causing their chemical poisoning, and, as a consequence, their slower growth.
|
|
KBA-8 |
KBA-10 |
|
Effective width, m |
8.2 |
10.2 |
|
Hourly performance, ha/h |
8.2 |
10.2 |
|
Operating speed, km/h |
Max. 12 |
Max. 12 |
|
Travelling speed, km/h |
20 |
20 |
|
Q-ty of operating elements, pcs |
16 |
20 / 22 |
|
Depth of cultivation, cm |
15-18 |
15-18 |
|
Overall dimensions in working position, mm Length Width Height |
13.5 8.2 2.1 |
13.5 10.2 2.1 |
|
Overall dimensions in travelling position, mm Length Width Height |
13.5 5.0 2.1 |
13.5 5.0 3.1 |
|
Storage trailer, m3 |
6 |
6 |
|
Weight, kg |
7000 |
8000 |
|
Mounting options |
Trailed |
Trailed |
|
Tractor power, h.p. (class) |
300 h.p. |
350 h.p. |